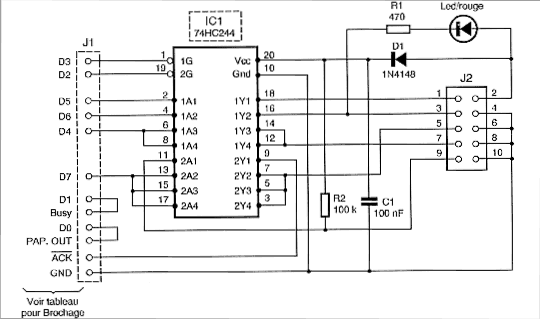
1. Transmitter
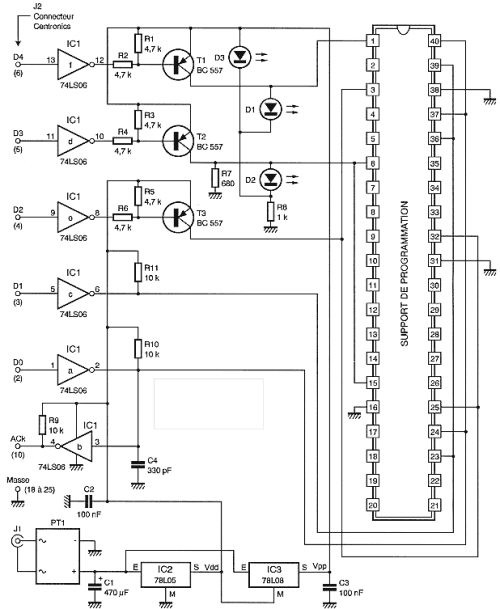
To relieve you of any concern related to high frequency, I used a module ready, in case a module Aurel audio FM transmitter. This tiny circuit board with 2 cm by 4 cm supports a transmitter modulation frequency track, delivering an RF power of 10 mW which is quite sufficient for the desired use. As it is driven by a resonator surface wave, its frequency stability is excellent.
As you can see the review of the scheme, the module can stand alone even for some HF itself since it lacks power and a network of pre-emphasis R7, R8, C6, designed to improve quality transmission of higher frequencies.

The input level required by the circuit to achieve a sufficient modulation rate of 100 mV rms, a preamplifier is necessary for our microphone. It is the role of IC1, mounted on a very classic inverting amplifier with adjustable gain through P1.
The provided microphone is a model electret with its supply circuit formed by R1, R2 and C1, but you might as well use a conventional dynamic mic, or an external electret microphone with its integrated power supply in which case R1, R2 and C1 disappear.
2. Receiver

In order not to saturate the amplifier or mixer that follows, the adjustable potentiometer P1 can measure the level applied to it.
This preamplifier is fed continuously as the module Aurel but instead receives its power through the leg 18 of the latter. This output is in fact controlled by the internal circuit noise and is connected to power when the circuit noise estimates have detected a valid issue. The operating threshold of the muffler is adjustable and is obviously the role of the potentiometer P2 is the only external control of the receiver.
The food in turn must be regulated to 5 volts, which is made by IC2 which can receive input from 9 to 15 volts from such amplifier associated with a block or sector-style outlet . The low power consumption of the arrangement (of the order of 30 mA) makes this power supply.
Read More → Rangkaian FM Wireless HI-FI
To relieve you of any concern related to high frequency, I used a module ready, in case a module Aurel audio FM transmitter. This tiny circuit board with 2 cm by 4 cm supports a transmitter modulation frequency track, delivering an RF power of 10 mW which is quite sufficient for the desired use. As it is driven by a resonator surface wave, its frequency stability is excellent.
As you can see the review of the scheme, the module can stand alone even for some HF itself since it lacks power and a network of pre-emphasis R7, R8, C6, designed to improve quality transmission of higher frequencies.
Schematic of the transmitter

The input level required by the circuit to achieve a sufficient modulation rate of 100 mV rms, a preamplifier is necessary for our microphone. It is the role of IC1, mounted on a very classic inverting amplifier with adjustable gain through P1.
The provided microphone is a model electret with its supply circuit formed by R1, R2 and C1, but you might as well use a conventional dynamic mic, or an external electret microphone with its integrated power supply in which case R1, R2 and C1 disappear.
2. Receiver
As to the transmitter, I used a module Aurel, which is an FM audio receiver. It also appears as a tiny circuit board containing all the components of the receiver, equipped with a squelch circuit or quiet as I put to good use.
As illustrated, the audio output takes place on the leg 10 of the module and should be désaccentuée through capacitor C4 to offset the effect of pre-emphasis circuit used in the show. The AF level issued by the module may be insufficient for some high fidelity amplifiers or mixers certain: it is only 100 mV in the best cases I amplifies a bit through rose IC1 very classic.
Schematic of receiverAs illustrated, the audio output takes place on the leg 10 of the module and should be désaccentuée through capacitor C4 to offset the effect of pre-emphasis circuit used in the show. The AF level issued by the module may be insufficient for some high fidelity amplifiers or mixers certain: it is only 100 mV in the best cases I amplifies a bit through rose IC1 very classic.

In order not to saturate the amplifier or mixer that follows, the adjustable potentiometer P1 can measure the level applied to it.
This preamplifier is fed continuously as the module Aurel but instead receives its power through the leg 18 of the latter. This output is in fact controlled by the internal circuit noise and is connected to power when the circuit noise estimates have detected a valid issue. The operating threshold of the muffler is adjustable and is obviously the role of the potentiometer P2 is the only external control of the receiver.
The food in turn must be regulated to 5 volts, which is made by IC2 which can receive input from 9 to 15 volts from such amplifier associated with a block or sector-style outlet . The low power consumption of the arrangement (of the order of 30 mA) makes this power supply.